Cell Parts And Functions Worksheet Answers Worksheets Samples
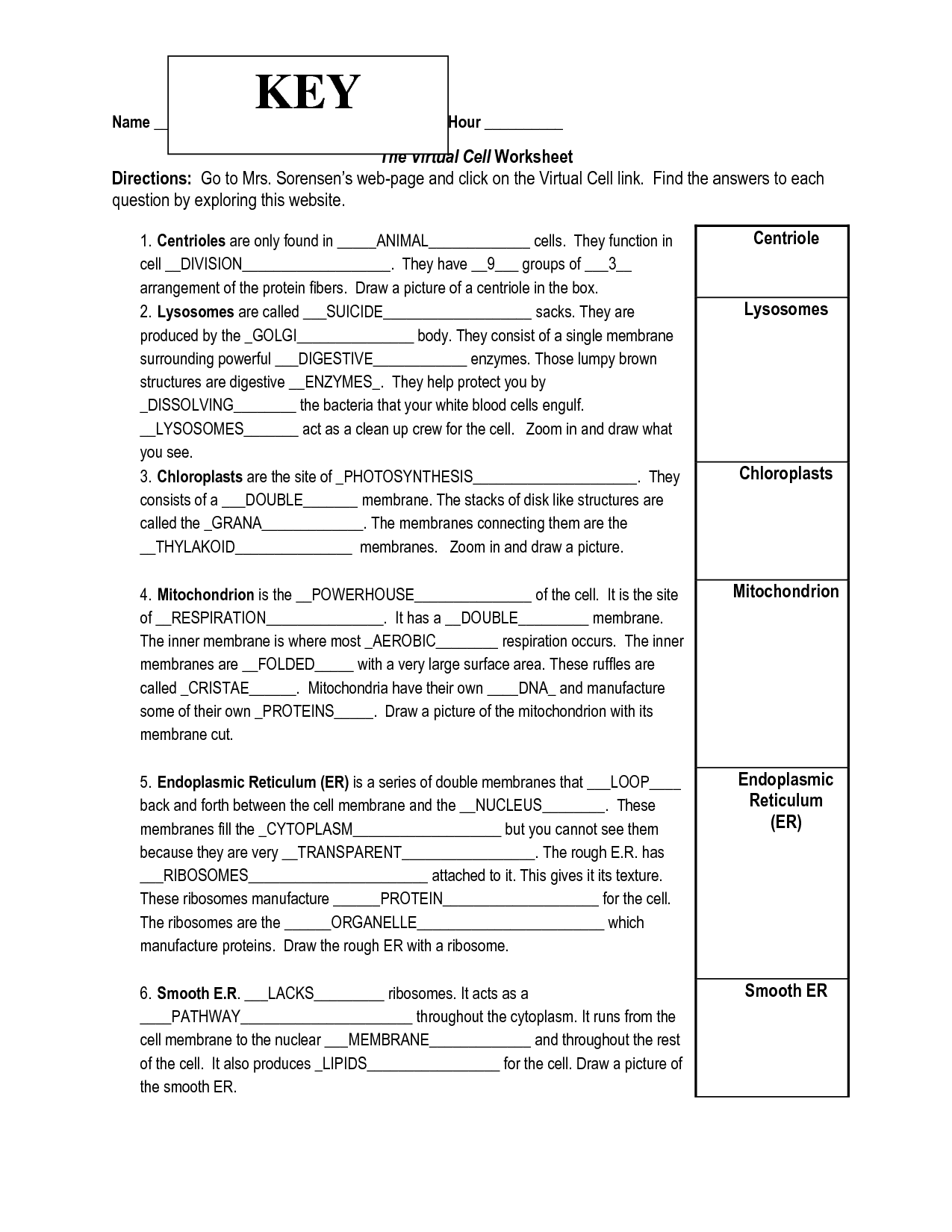
1. Plasma membrane: a selective barrier which encloses a cell (plant and bacteria cells also contain a cell wall ). 2. Cytosol: located inside the plasma membrane, this is a jelly-like fluid that supports organelles and other cellular components. 3. Cytoplasm: the cytosol and all the organelles other than the nucleus. 4.

39 cell structure and function worksheet answer key Worksheet Database
Unit 1 Chemistry of life. Unit 2 Cell structure and function. Unit 3 Cellular energetics. Unit 4 Cell communication and cell cycle. Unit 5 Heredity. Unit 6 Gene expression and regulation. Unit 7 Natural selection. Unit 8 Ecology. Unit 9 Worked examples of AP®︎ Biology free response questions.
Student Exploration Cell Structure Asnwer Key To start, click sample
SAMPLE ANSWER: Every structure and organelle in a cell carries out certain processes, such as making or storing substances, that help the cell stay alive. SAMPLE ANSWER: A cell can transport materials across the membrane through passive transport, which does not require energy. A cell can move materials by active transport, which needs energy.

14 Best Images of Cell Structure And Function Worksheet Answers Cell
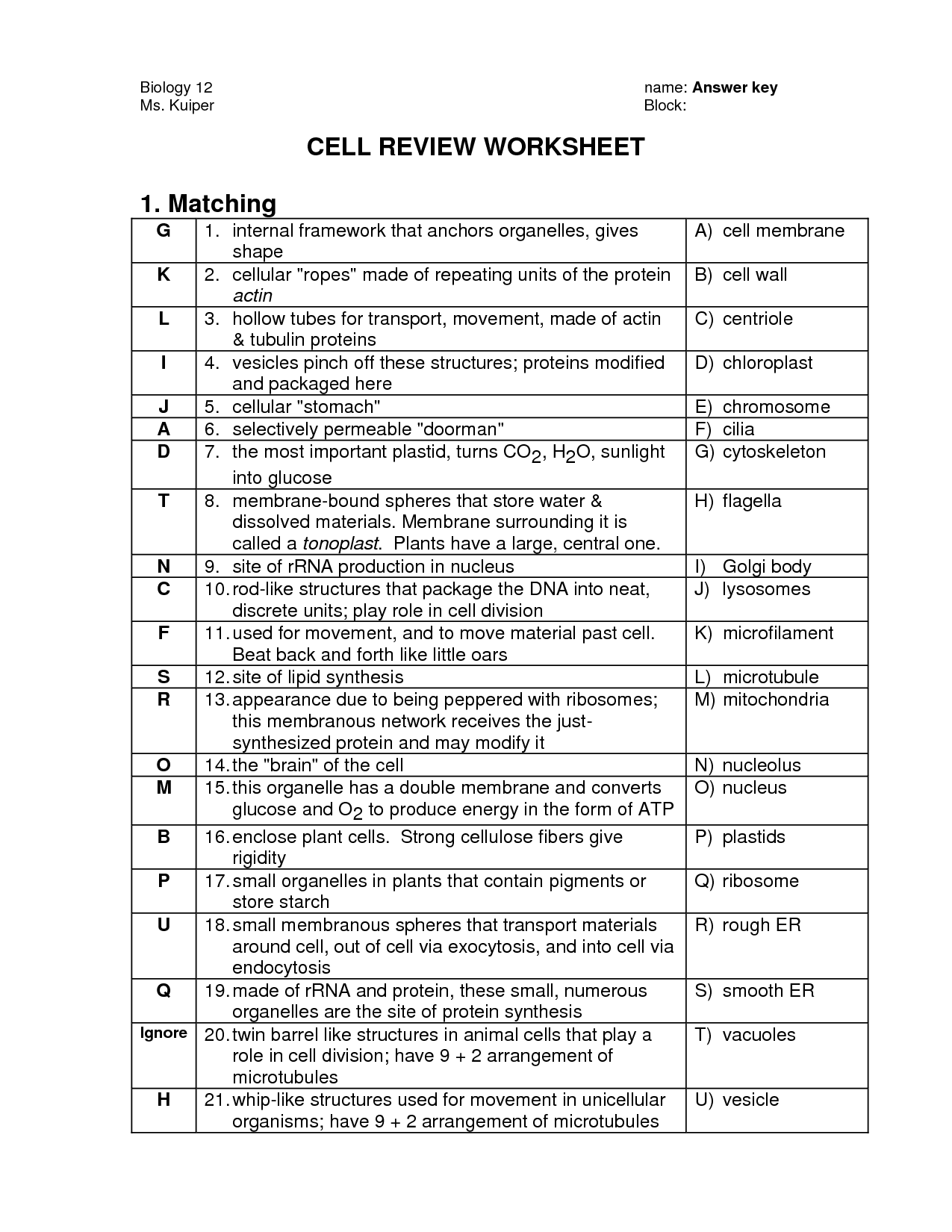
a. The three structures that provide support and protection in the eukaryotic cell are: i. Cell membrane ii. Cell wall (outside of the cell membrane) iii. Microtubules (found in cytoskeleton) Identify A and B in the slide image below. Onion root tip, 1000x. A: ________A is pointing to the chromosomes ______________

Accounting Chapter 7 Study Guide
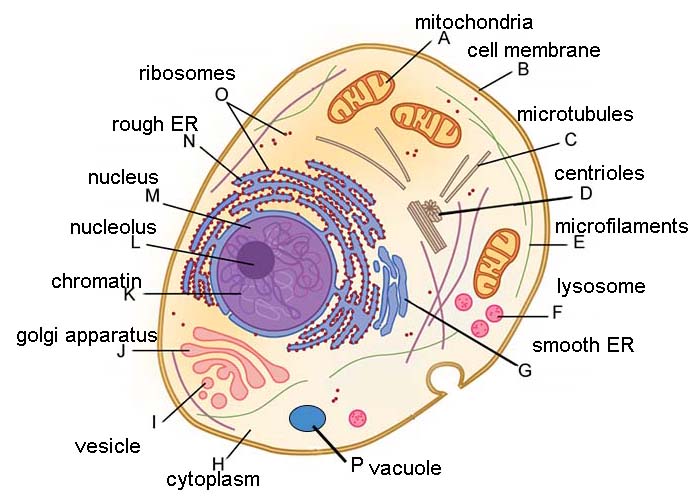
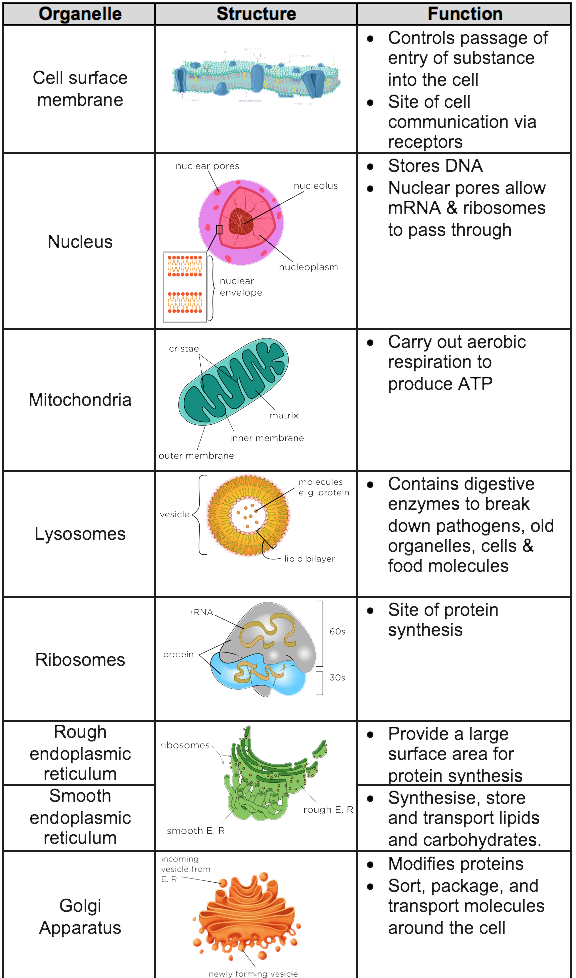
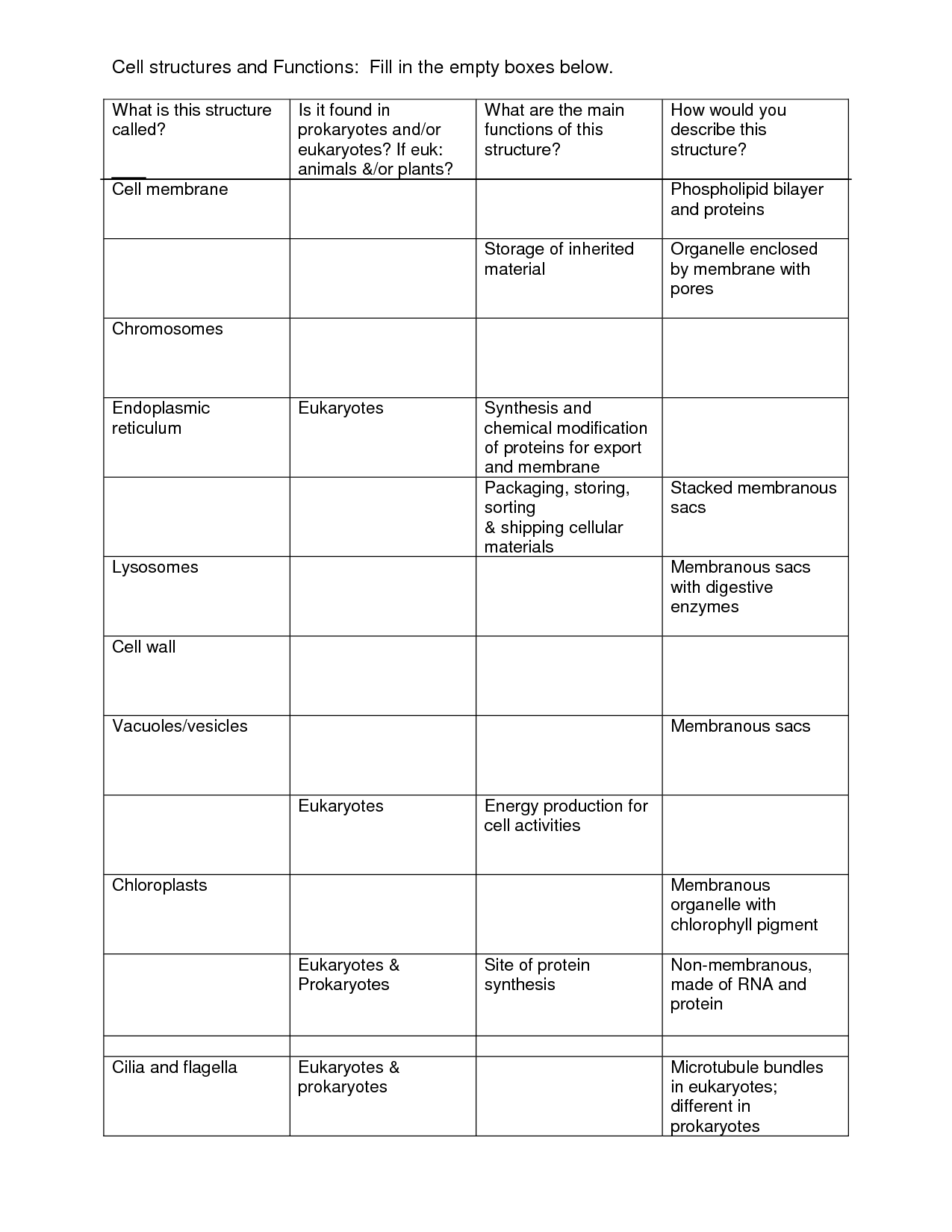
Key Concept ' What are the functions of the major cell structures? Comparing a Cell to a Factory (page 174) 1. What is an organelle? It is a structure in eukaryotic cells that acts as if it is a specialized organ. 2. Label the structures on the illustrations of the plant and animal cells. Nucleolus Nucleus Nuclear envelope Centrioles.

Answer Key Reading essentials c.2 Cell Structure and Function
smooth endoplasmic reticulum (SER) the region of the endoplasmic reticulum that has few or no ribosomes on its cytoplasmic surface and synthesizes carbohydrates, lipids, and steroid hormones; detoxifies chemicals like pesticides, preservatives, medications, and environmental pollutants, and stores calcium ions.
Cell Structure And Function Worksheet With Answers
All organisms contain prokaryotic cells. B) Cells arise only from previously existing cells. C) Cells are the basic unit of structure for all living organisms. D) All living organisms are composed of one or more cells. 2: A ____ contains polar and nonpolar ends, forming the plasma membrane.
Chapter 3.4 Membrane Structure and Function How do substances
Today, the cell theory,which states that all organ-isms are made up of basic living units called cells and that cells come only from preexisting cells, is a basic theory of biology. The cell theory states the following: All organisms are composed of one or more cells. Cells are the basic living unit of structure and function in organisms.

12 Best Images of Modern Biology Worksheet Answers Metric System
NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 8 Cell Structure and Functions are prepared by the team of our subject experts to assist students in their school assignments and exam preparation. BYJU'S provides free NCERT Solutions for all the classes and subjects in a chapter-wise format.

33 Cells And Cell Organelles Worksheet Answers support worksheet
3.1: How Cells Are Studied. In multicellular organisms, several cells of one particular kind interconnect with each other and perform shared functions to form tissues (for example, muscle tissue, connective tissue, and nervous tissue), several tissues combine to form an organ (for example, stomach, heart, or brain), and several organs make up.
14 Best Images of Cell Structure And Function Worksheet Answers Cell
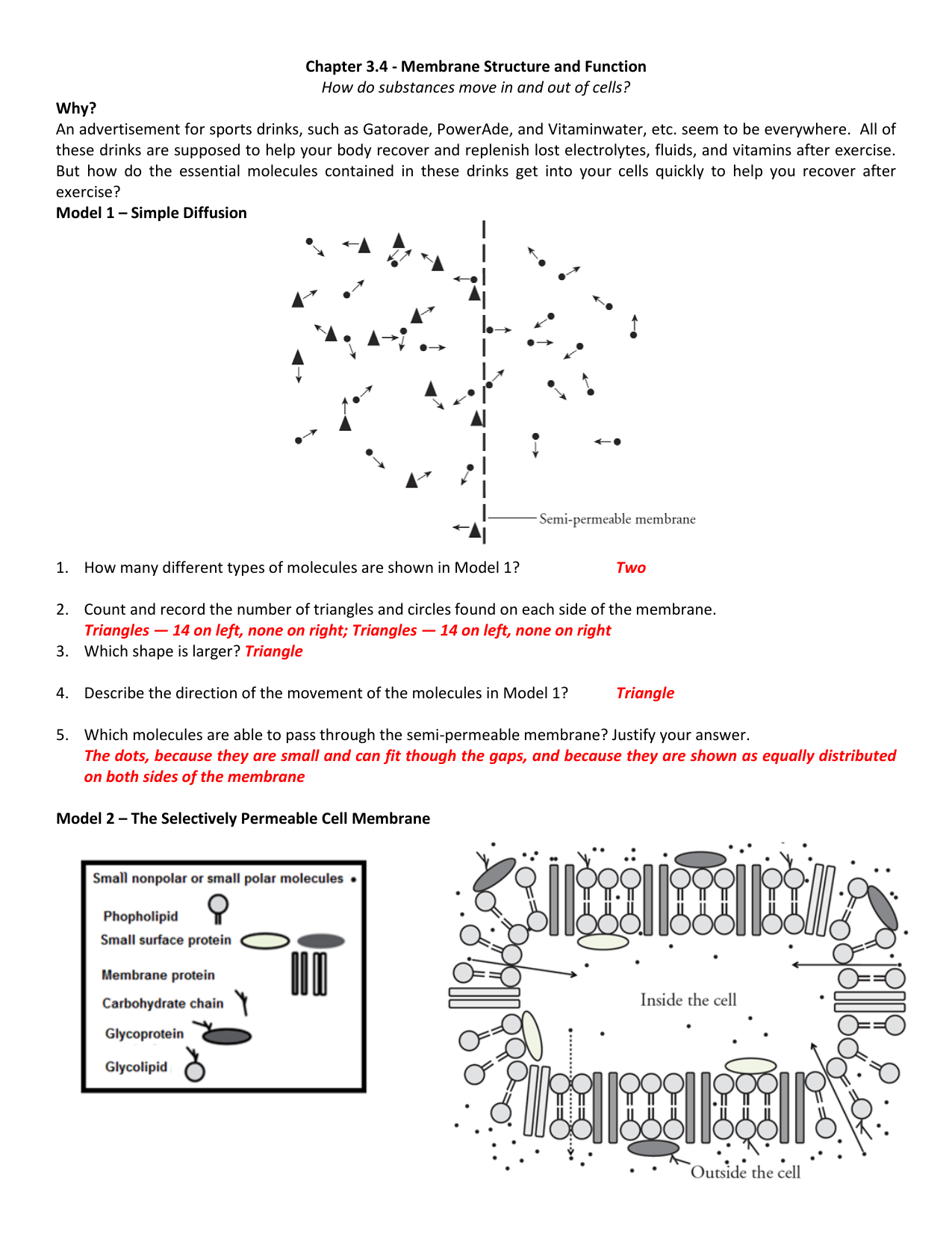
The cell membrane is an extremely pliable structure composed primarily of back-to-back phospholipids (a "bilayer"). Cholesterol is also present, which contributes to the fluidity of the membrane, and there are various proteins embedded within the membrane that have a variety of functions.
4 Cell Structure And Function Biology Notes For A Level
A cell is the smallest living thing in the human organism, and all living structures in the human body are made of cells. There are hundreds of different types of cells in the human body, which vary in shape (e.g. round, flat, long and thin, short and thick) and size (e.g. small granule cells of the cerebellum in the brain (4 micrometers), up to the huge oocytes (eggs) produced in the female.

Chapter 7 Cell Structure And Function Concept Map Answer Key US
Unit 3 FRQ (Commercial Fertilizers) Answers. 3 min read. Unit 6 FRQ (Genetic Expression) with Feedback. Cell Structure and Function. written by Kari Parnin. AP Biology Cram Unit 2: Cell Structure and Function. written by Kari Parnin. 🌶️ AP Bio Cram Review: Unit 3: Cellular Energetics. written by Jessica Nadzam.
14 Best Images of Cell Structure And Function Worksheet Answers Cell
theory that states that all organisms are made of cells, all cells are produced by other living cells, and the cell is the most basic unit of life. cytoplasm. jellylike substance inside cells that contains molecules and in some cells organelles. organelle. membrane-bound structure that is specialized to perform a distinct process within a cell.

Cell Structure SE 1 Cell Structure *Answer Questions ON YOUR OWN
AP Biology Unit 2: Cell Structure & Function Topics - Cell Structure: Subcellular Components, Cell Structure and Function, Cell Size, Plasma Membranes, Membrane Transport, Facilitated Diffusion, Tonicity and Osmoregulation, Mechanisms of Transport, Cell compartmentalization, Origins of Cell Compartmentalization Directions - For each question, ch.
18 Cell Organelle Worksheet.pdf /
A. Structure that organizes motion of chromosomes. B. Stack of membranes that packages chemicals. C. Membrane that protects the nucleus. D. Membrane that surrounds and protects the cell. E. Sac filled with digestive chemicals. F. Structures that converts nutrients to energy. G.
